Researchers at UCLA report that they have refined a method they previously developed for capturing and analyzing cancer cells that break away from patients' tumors and circulate in the blood. With the improvements to their device, which uses a Velcro-like nanoscale technology, they can now detect and isolate single cancer cells from patient blood samples for analysis.
Circulating tumor cells, or CTCs, play a crucial role in cancer metastasis, spreading from tumors to other parts of the body, where they form new tumors. When these cells are isolated from the blood early on, they can provide doctors with critical information about the type of cancer a patient has, the characteristics of the individual cancer and the potential progression of the disease. Doctors can also tell from these cells how to tailor a personalized treatment to a specific patient.
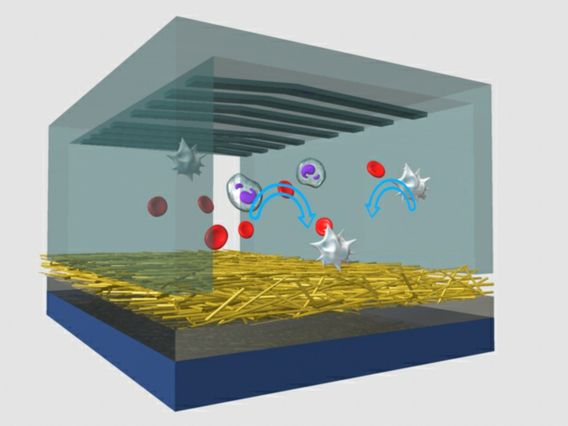
In recent years, a UCLA research team led by Hsian-Rong Tseng, an associate professor of molecular and medical pharmacology at the Crump Institute for Molecular Imaging and a member of both the California NanoSystems Institute at UCLA and UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, has developed a "NanoVelcro" chip. When blood is passed through the chip, extremely small "hairs" — nanoscale wires or fibers coated with protein antibodies that match proteins on the surface of cancer cells — act like Velcro, traping CTCs and isolating them for analysis.
CTCs trapped by the chip also act as a "liquid biopsy" of the tumor, providing convenient access to tumor cells and earlier information about potentially fatal metastases.
Histopathology — the study of the microscopic structure of biopsy samples — is currently considered the gold standard for determining tumor status, but in the early stages of metastasis, it is often difficult to identify a biopsy site. By being able to extract viable CTCs from the blood with the NanoVelcro chip, however, doctors can perform a detailed analysis of the cancer type and the various genetic characteristics of a patient's specific cancer.
Improving the NanoVelcro device
Tseng's team now reports that they have improved the NanoVelcro chip by replacing its original non-transparent silicon nanowire substrate inside with a new type of transparent polymer nanofiber-deposited substrate, allowing the device's nanowires to better "grab" cancer cells as blood passes by them.
Tseng and his colleagues were able to pick single CTCs immobilized on the new transparent substrate by using a miniaturized laser beam knife, a technique called laser micro-dissection, or LMD.
The researchers' paper on their improvement to the chip was published online Feb. 22 in the peer-reviewed journal Angewandte Chemie and is featured on the cover of the journal's March 2013 print issue.
"This paper summarizes a major milestone in the continuous development of NanoVelcro assays pioneered by our research group," Tseng said. "We now can not only capture cancer cells from blood with high efficiency but also hand-pick single CTCs for in-depth characterization to provide crucial information that helps doctors make better decisions."
Testing the improvements on melanoma
Using the new assay on patients' blood containing circulating melanoma cells (CMCs), Tseng's team was able to isolate and preserve single CMCs. Melanoma is a deadly type of skin cancer that is prone to spreading quickly throughout the body. The ability to capture and preserve single CMCs allows doctors to analyze melanoma cells' DNA structure, determine the genetic characteristics of the patient's cancer and confirm that the circulating cells remain genetically similar to the tumor they came from.
The preservation of single captured CMCs in this proof-of-concept study also allowed researchers to conduct an analysis — called single-cell genotyping — to find within the cell a specific target (BRAF V600E) for a drug called vemurafenib. BRAF V600E is a mutation in the BRAF protein that appears in approximately 60 percent of melanoma cases. Drugs that inhibit BRAF are able to slow and often reverse the growth of melanoma tumors.
"With this technology, we are getting closer to the goal of a widely clinically applicable liquid biopsy, where we can sample cancer cells by a simple blood draw and understand the genes that allow them to grow," said Dr. Antoni Ribas, a professor of medicine in the division of hematology–oncology, a Jonsson Cancer Center member and one of Tseng's key collaborators. "With the NanoVelcro chips, we will be able to better personalize treatments to patients by giving the right treatment to stop what makes that particular cancer grow."
Dr. Roger Lo, another key Tseng collaborator and an assistant professor in UCLA's department of medicine, division of dermatology, and department of molecular and medical pharmacology, was also optimistic about the new method.
"This scientific advancement — being able to capture the melanoma cells in transit in the blood and then perform genetic analysis on them — will in principle allow us to track the genomic evolution of melanoma under BRAF-inhibitor therapy and understand better the development of drug resistance," said Lo, who is also a member of the Jonsson Cancer Center.
UCLA's Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center has more than 240 researchers and clinicians engaged in disease research, prevention, detection, control, treatment and education. One of the nation's largest comprehensive cancer centers, the Jonsson Center is dedicated to promoting research and translating basic science into leading-edge clinical studies. In July 2012, the Jonsson Cancer Center was once again named among the nation's top 10 cancer centers by U.S. News & World Report, a ranking it has held for 12 of the last 13 years.
For more news, visit the UCLA Newsroom and follow us on Twitter.